PHASE IV MULTIBODY DYNAMICS




UM CAD Interfaces
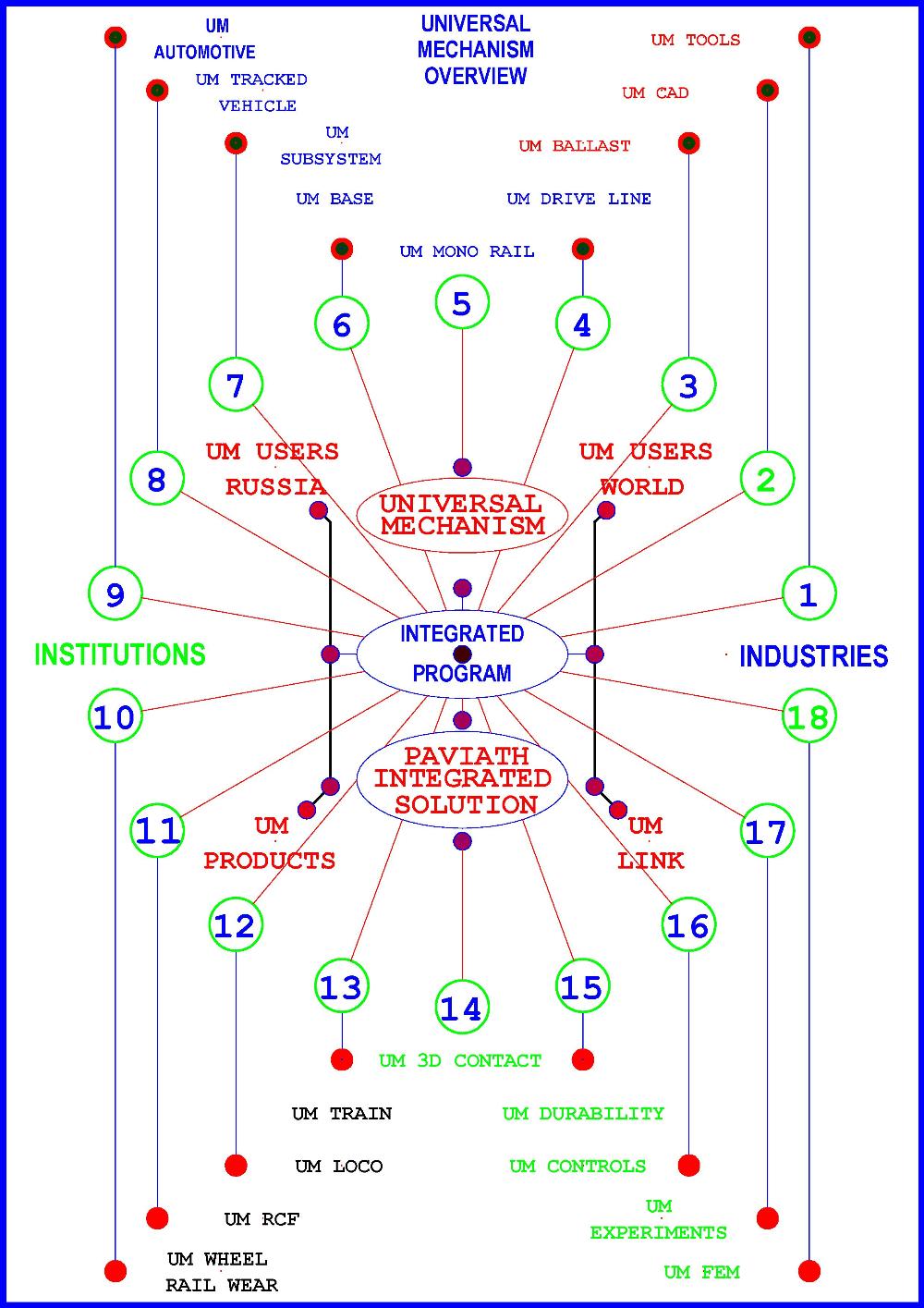
The CAD Interfaces Module (UM CAD Interfaces) - Workflow - Method 1 - Method 2 - KOMPAS 3D - Autodesk Inventor - SolidWorks - Unigraphics NX - Conversion of STEP, IGES, X_T, SAT formats

Universal Mechanism consists of different modules and tools and may be delivered in the different configurations. The minimal, so called "base configuration" (UM Base), is a ready tool which allows carrying out dynamic analysis of mechanical systems. Functionality of the base configuration can be widened with the help of additional modules.
| UM Automotive | UM Loco | UM Train | UM Tracked Vehicle | UM FEM | UM CAD Interfaces |
| UM Experiments | UM Control | UM Subsystems | UM Durability | UM Ballast | UM 3D Contact |
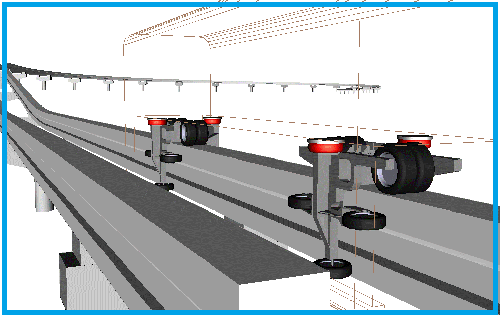
UM Automotive includes mathematical models of tires, program tools for description of road plan and road excitations. UM Automotive includes as well set of typical maneuvers, suspensions, steering systems and elements of trasmission. Module gives user the possibility to estimate dynamical behavior of the vehicle, including forces in the suspension force elements, safety and "road holding" factors, etc...
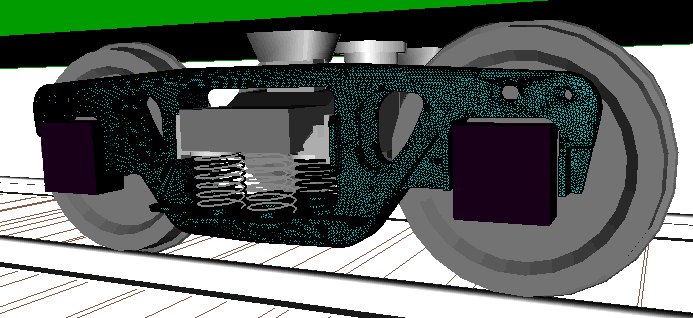
The program package includes module UM Loco intended for simulation of railway vehicle dynamics in both straight and curve railroad tracks. The simulation is performed in time domain by means of numeric integration of differential or differential-algebraic equations of motion. UM Loco allows the user to create fully parameterized models of vehicles...
UM Train module automates the process of train model creation and the analysis of obtained results. The module allows computing the longitudinal dynamics of train in braking, traction and idling modes on a railway track of any configuration...
The UM Tracked Vehicle module of UM software has been developed for an automatic generation of models of tracked vehicles and analysis of their dynamics...
This module let the user a possibility to introduce into a mechanical system deformable bodies undergo large reference displacement but small deformation. Such an approach makes more exact results in comparison with multibody simulation and could be very useful in some cases. This approach could be useful for research of vibration of car body and carriage underframe during the motion of railway vehicle subject to influence from railway track irregularities and a power generating set..
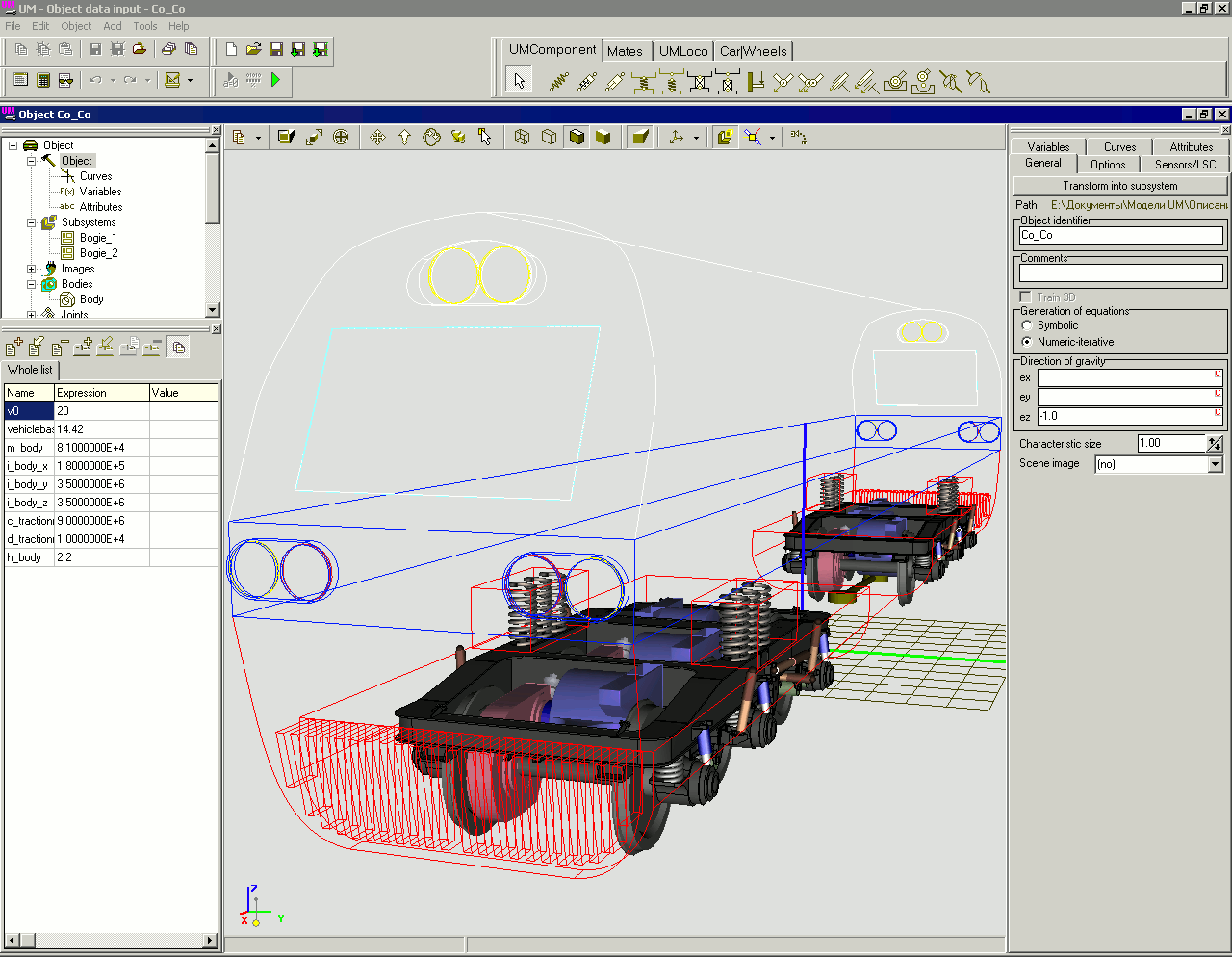
Modern approach to design of machines and mechanisms assumes creating 3D models with the help of one of the computer-aided design (CAD) software with parallel strength and dynamics analysis. To simplify importing such models from CAD software to Universal Mechanism we developed tools for direct data import from CAD software to Universal Mechanism. Such import tools are collected within the UM CAD Interfaces module. The current UM version supports data import from Autodesk Inventor, SolidWorks, Unigraphics NX, KOMPAS and Pro/ENGINEER...
It is often required in engineering practice to carry out series of numerical experiments, for example to analyze dynamical behavior and sensitivity of mechanical system or to find out optimal parameters of the system. UM Experiments gives a user a possibility to run series of numerical experiments automatically...
Universal Mechanism includes UM Control module, which provides interface between Universal Mechanism and Matlab/Simulink. The user can compile his/her own Matlab/Simulink model and attach it into the Universal Mechanism. Matlab/Simulink interface gives the user a possibility to include unlimited number of Matlab/Simulink libraries and interactively turn on/off interfaces...
Subsystem technique is a basis of modeling objects with large number of degrees of freedom and creation of database of typical design elements for modeling technical systems. By using this method an object is represented as a tree of subsystems, which are linked by means of force elements and constraints. Any object previously created by the user can be a subsystem. This object may contain any tree of subsystems...
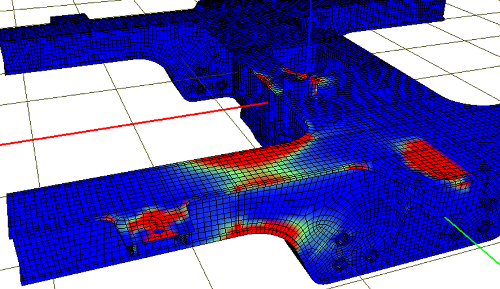
The fatigue analysis starts with the dynamical hybrid model in Universal Mechanism. The flexibility characteristics of the structural parts are incorporated into UM model using a modal formulation based upon component mode synthesis. Basically, this method represents the part,s flexibility using a modal basis, which is optimized to account for constraint and force locations. The mode shape displacements and stresses are calculated using the finite element software. The UM Durability module combines the stress time history information generated during series of numerical experiments in UM and the material fatigue strength characteristics to generate the predicted life distribution in the part...
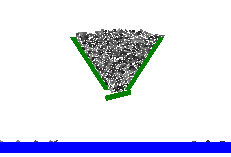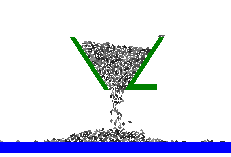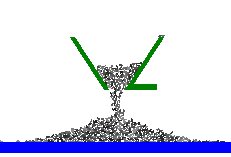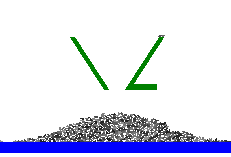
This module allows including in a UM model a planar granular media, which is a set of particles (rigid polygons and circles). The particles interact with each other by contact forces. Simple models of contact forces are used in the module. Each force consists of two components. The first component is a linear viscoelastic normal force. Another one is a dry friction force with two modes: sliding and sticking...
This module allows simulating of contact interaction of bodies by contact manifolds (graphical objects). The realized contact algorithm is based on the simulation of interaction of arbitrary convex polyhedrons. The set of supplied primitives includes the following types: box, cylinder, cone, ellipsoid, and polyhedron




